

Connect drive directly to PATA/SATA interface do not use USB, Firewire, etc.If you must use a version prior to 9.31, you'll want to increase the timeout by changing const int timeout_2hrs = (2 * 60 * 60) in the source code to something like const int timeout_6hrs = (6 * 60 * 60) and recompiling, as explained by KnifeWrench.Boot from RIP Linux † or any distro which includes hdparm 9.31 or greater (prior versions would timeout after 2 hours, leaving the disk only partially erased).block erase wiping tools like DBAN) is often cited, the difference is negligible.
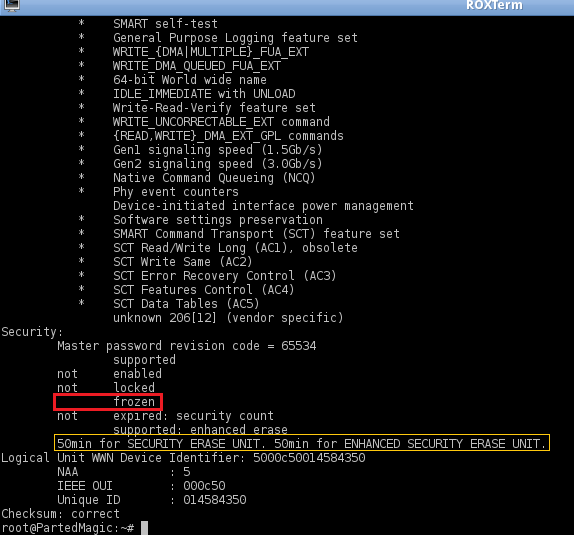 Overwrites blocks marked as bad by the hard drive (which DBAN and similar tools ignore). hdparm/ Linux offers much better hardware support than HDDErase/ MS-DOS. Reportedly restores peak performance to SSD drives (though SE fails to securely wipe some SSDs). Can securely wipe most PATA/SATA hard drives manufactured this century. It completes in about 1/8 the time of 5220 block erasure." The guidelines also state that "degaussing and executing the firmware Secure Erase command (for ATA drives only) are acceptable methods for purging." Benefits Is a drive command defined in the ANSI ATA and SCSI disk drive interface specifications, which runs inside drive hardware. Beware - When SECURE ERASE doesn't erase at allĪccording to National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-88: Guidelines for Media Sanitization, Secure Erase is "An overwrite technology using firmware based process to overwrite a hard drive. Moreover, as the hdparm manpage explains, "these switches are DANGEROUS to experiment with, and might not work with every kernel. The instructions below will irretrievably destroy data. See also ATA Sanitize Device and hdparm, NVMe Secure Erase, and NVMe Sanitize in this series. ATA Secure Erase (SE) and hdparm / docs / ATA Secure Erase (SE) and hdparm
Overwrites blocks marked as bad by the hard drive (which DBAN and similar tools ignore). hdparm/ Linux offers much better hardware support than HDDErase/ MS-DOS. Reportedly restores peak performance to SSD drives (though SE fails to securely wipe some SSDs). Can securely wipe most PATA/SATA hard drives manufactured this century. It completes in about 1/8 the time of 5220 block erasure." The guidelines also state that "degaussing and executing the firmware Secure Erase command (for ATA drives only) are acceptable methods for purging." Benefits Is a drive command defined in the ANSI ATA and SCSI disk drive interface specifications, which runs inside drive hardware. Beware - When SECURE ERASE doesn't erase at allĪccording to National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-88: Guidelines for Media Sanitization, Secure Erase is "An overwrite technology using firmware based process to overwrite a hard drive. Moreover, as the hdparm manpage explains, "these switches are DANGEROUS to experiment with, and might not work with every kernel. The instructions below will irretrievably destroy data. See also ATA Sanitize Device and hdparm, NVMe Secure Erase, and NVMe Sanitize in this series. ATA Secure Erase (SE) and hdparm / docs / ATA Secure Erase (SE) and hdparm






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
